
|

|
||

|

|

|

|
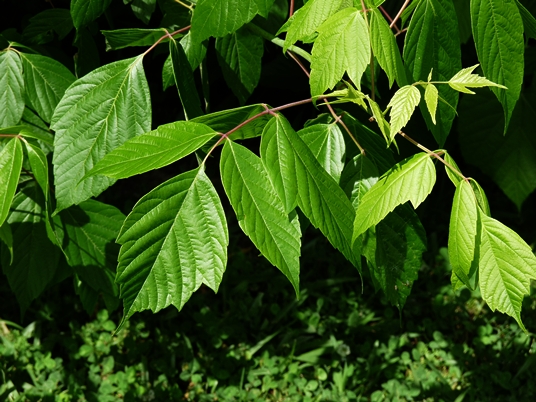
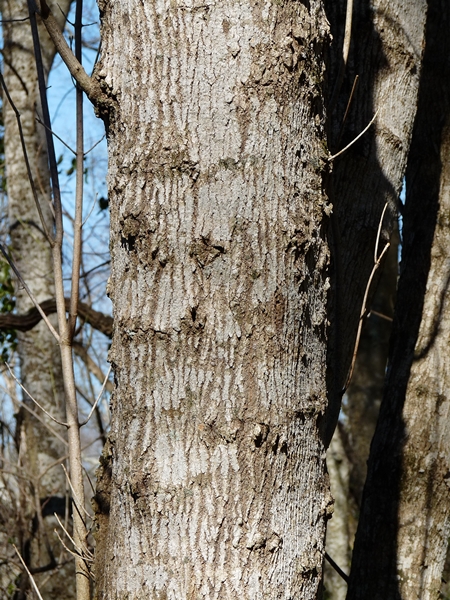
Box Elder (Acer negundo), also called ash-leaved maple, is a small to medium-sized tree, usually less than 50 feet but occasionally becoming 75 feet in height, with a trunk 2 to 4 feet in diameter; the bole is usually short and divides 6 to 20 feet above the ground into several stout, horizontal limbs and branches to form a wide, rounded, bushy crown. The National Champion has a circumference of 21.67 feet, height of 76 feet, and an average crown spread of 67 feet. Acer negundo is of some value in the manufacture of cheap wooden products; widely planted as an ornamental and for windbreaks (see range in the midwest). The species name "negundo" is from a Sanskrit name for the Vitex negundo, referring to the likeness of leaves to this species of Vitex.
Separating Characteristics
The two best characteristics for separating box elder from the other maples are the leaves and the twigs. A. negundo has compound leaves, while all other maples in this treatment have simple leaves. The leaves usually have 3-7 leaflets, but can have as many as 9. The twigs are lustrous or glaucous, green to purplish green, with scattered pale lenticels. Other maples usually have brown or red twigs. Another character that may be valuable is the trees tendency to retain the fruit stalks throughout winter.
Habitat
Riverbanks, swamps, bottomlands, also upslope on calcareous substrates. The species ranges nearly across North America, including well into the arid west along rivers. A. negundo often grows on the banks of rivers, leaning out over the water at a 45 degree angle. The leaves can resemble poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans), which has alternate leaves. The coarse toothing (approaching lobing) distinguishes it readily from any of our ashes (Fraxinus).
Habitat information from:
Weakley, Alan S., Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States, Working Draft of 21 May 2015.
Native Range
Box elder has a tremendously large range. It is found from New England south to Florida, west to Texas and north of midwestern Canada and is scattered through the west to California and south to Mexico and Central America.
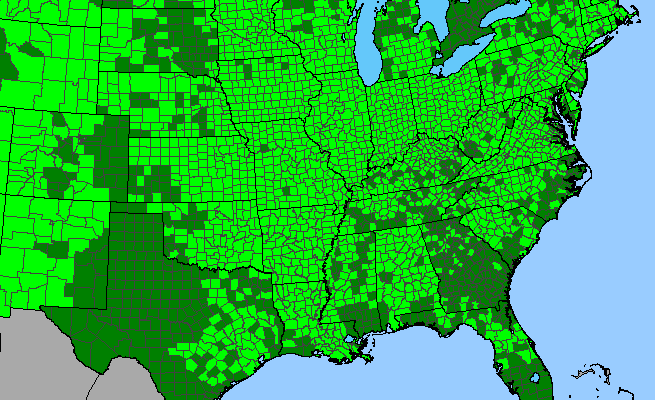
The native range of Acer negundo (Box Elder)
Kartesz, J.T., The Biota of North America Program (BONAP). 2015. North American Plant Atlas. (http://bonap.net/napa). Chapel Hill, N.C. [maps generated from Kartesz, J.T. 2015. Floristic Synthesis of North America, Version 1.0. Biota of North America Program (BONAP). (in press)].
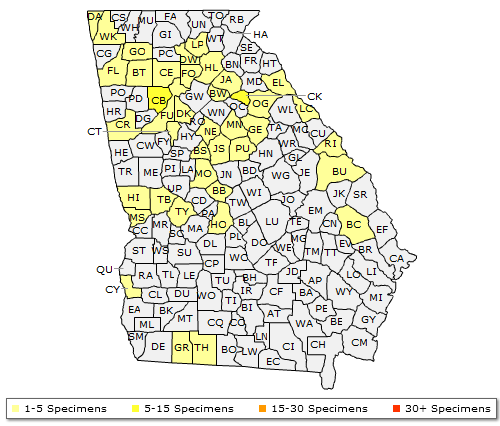
The Georgia range of Acer negundo (Box Elder)
Zomlefer, W.B., J.R. Carter, & D.E. Giannasi. 2014 (and ongoing). The Atlas of Georgia Plants. University of Georgia Herbarium (Athens, Georgia) and Valdosta State University Herbarium (Valdosta, Georgia). Available at: http://www.georgiaherbaria.org/.
Guide to the Trees of North Georgia and Adjacent States
Web Page © Richard Ware
send Richard an E-mail