
|

|

|

|
OLEACEAE - - Olive Family

|

|

|

|
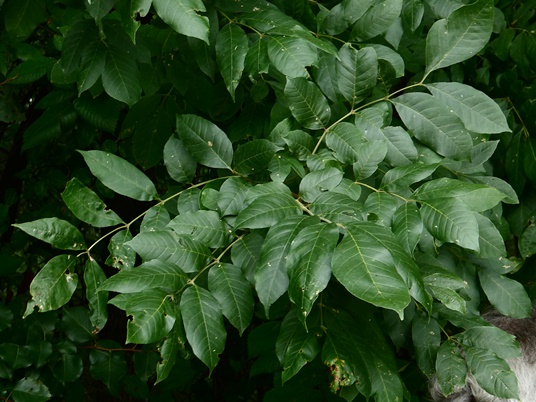
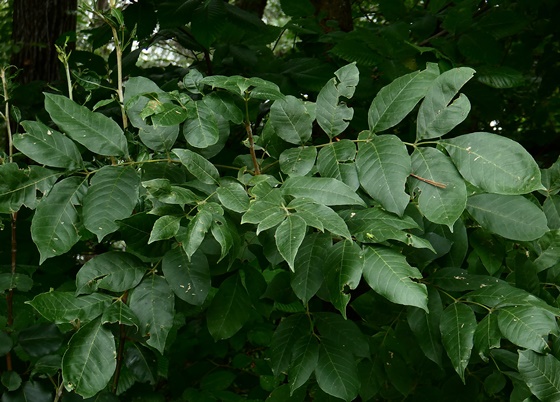
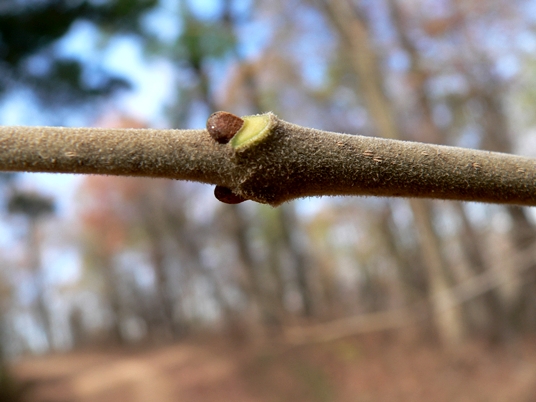
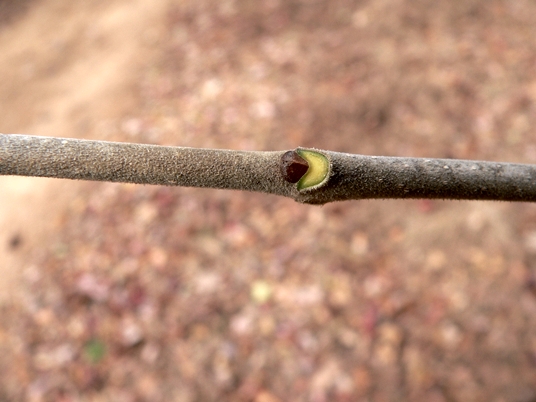
Biltmore Ash (Fraxinus biltmoreana) - A large tree of sporadic but widespread range. Although often synonymized with White Ash, the velvety twigs of Biltmore Ash lack the characteristic notched leaf scar so often used to distinguish the former species. Biltmore Ash also varies by its tendency to have brown bark with a softer or corkier texture and a denser, more rounded crown when open grown. Fruit 3—4.5cm long, sometimes with a proportionately then in White Ash.
Mesic slopes, rich cove forests, dry calcareous or mafic glades and woodlands (with Juniperus virginiana var. virginiana and Carya glabra).
Habitat information from:
Weakley, Alan S., Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States, Working Draft of 21 May 2015.
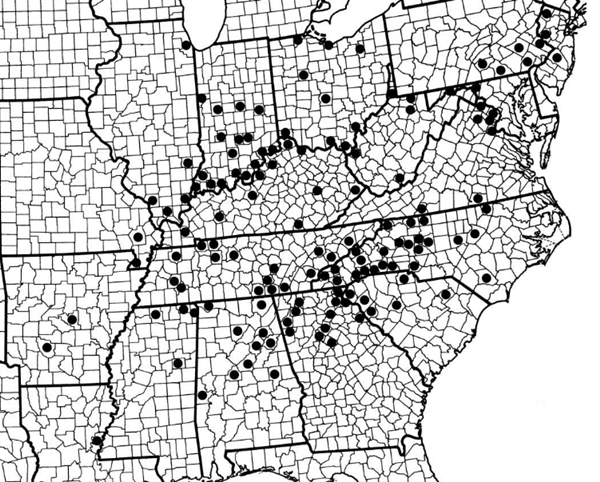
The range of Fraxinus biltmoreana (Biltmore Ash)
Nesom, G.L. 2010. Fraxinus biltmoreana and Fraxinus smallii (Oleaceae), forest trees of the eastern United States. Phytoneuron 2010-51: 1–30.
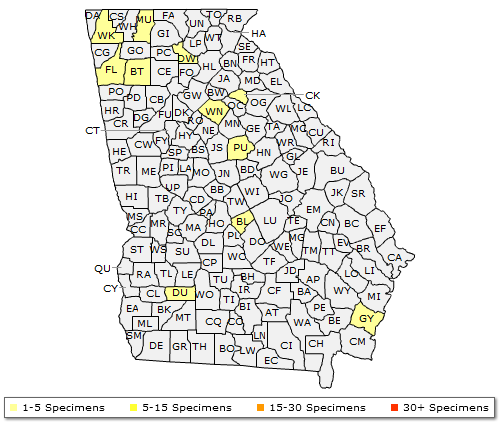
The Georgia range of Fraxinus biltmoreana (Biltmore Ash)
Zomlefer, W.B., J.R. Carter, & D.E. Giannasi. 2014 (and ongoing). The Atlas of Georgia Plants. University of Georgia Herbarium (Athens, Georgia) and Valdosta State University Herbarium (Valdosta, Georgia). Available at: http://www.georgiaherbaria.org/.
Guide to the Trees of North Georgia and Adjacent States
Web Page © Richard Ware
send Richard an E-mail